Slot Props Vue
Vue/prop-name-casing; vue/require-default-prop; vue/require-prop-types; vue/singleline-html-element-content-newline; vue/v-bind-style; vue/v-on-style; vue/v-slot-style; Priority B: Strongly Recommended for Vue.js 3.x. Vue/require-explicit-emits; Priority C: Recommended. Vue/attributes-order; vue/component-tags-order; vue/no-lone-template; vue. Slot='someslot' slot-scope='props'.
Props and $emit
When using Vue to develop a project, we divide the content of the project into modules, but sometimes there is data interaction between modules. In real project development, father-son and brother components need to pass values to each other. The most traditional way to pass values is props and $emit.
I. Props
Prop is some custom features that you can register on components. When a value is passed to a prop feature, it becomes an attribute of that component instance. To pass a title to the blog component, we can include it in the list of acceptable props for the component with a props option.
1. Examples of props passing values
Different parameters can also be passed to subcomponents:
2. Pros type validation
If we want each prop to have a specified value type and list prop as an object, the names and values of these properties are prop's respective names and types.
To make passing values more flexible, vue provides the following props authentication methods:
If a requirement is not met, Vue will warn you in the browser console. This is especially helpful in developing a component that will be used by others.
Note:
- All props make a single downlink binding between their father and son props: updates to the parent prop flow downward to the child components, but not vice versa. This prevents accidental changes in the state of the parent component from the child component, resulting in incomprehensible data flow to your application.
- Note that those props are validated before a component instance is created, so the properties of the instance (such as data, computed, etc.) are not available in default or validator functions.
- Because components cannot always predict the parameters that other components will pass in when they call the current component, vue also allows components to pass in some non-props features when they are called. These features are automatically added to the root element of the component.
2. $emit
A child component is called by a parent component. When a child component triggers a function, it needs a parent component response, using $emit.
1. $emit simple example
We can also throw some data to the outside world when we throw an event.
If a component throws more than one data when throwing an event, it can continue to pass a value to $emit in the form of a parameter list, and then call it in the form of a parameter list in the parent component. But when there is a lot of data, it makes the code seem lengthy, so we recommend that all the data to be thrown be integrated into one object and passed in an object to the second parameter of the $emit function.
Slot slot slot
Slot is the second way that components are called, which improves the reusability of components.
When the child component calls the parent component and transfers its value, it tends to transfer in the data layer, but sometimes we hope that the child component can respond better to one of its parent components in the structure rendering layer, and the content of the child component can be rendered through the data control of the parent component.
If we need an operation result prompt box, the title, picture and button bar in the bullet box all render the concrete result according to the operation result. Using props or $emit can also achieve this effect, but if the results of multiple rendering are very different, then the code redundancy goes up again, so Vue provides a more concise way, that is, slots.
A slot is equivalent to encapsulating a component into a large framework. As for what and how to display it, it can transfer data when invoked, control it by data, and display the incoming content when invoked.
1. Small examples of slots
Note:
If the Alert component does not contain a < slot > element, anything between the start tag and the end tag will be discarded when the component is called.
Vue Slot Props 違い
2. Setting up backup slots for components
If a slot is reserved in a component, but the content is not distributed when the component is called, it may lead to some unpredictable errors in structure and logic, so sometimes it is necessary to set a default content for the slot.
3. Named sockets
To encapsulate a component with high reusability, a slot may not be enough. We can reserve multiple slots for each slot at different locations of the component structure, name each slot, and distribute the corresponding content to different slots when calling the component. This is the named slot.
Call the Alert component:
Slot Props Vue Free
Abbreviation of Named Slot:
Note:
- There is no < slot > with the name attribute set, and the default name value is default.
- The v-slot attribute can only be added to one < template > (except for exclusive default slots).
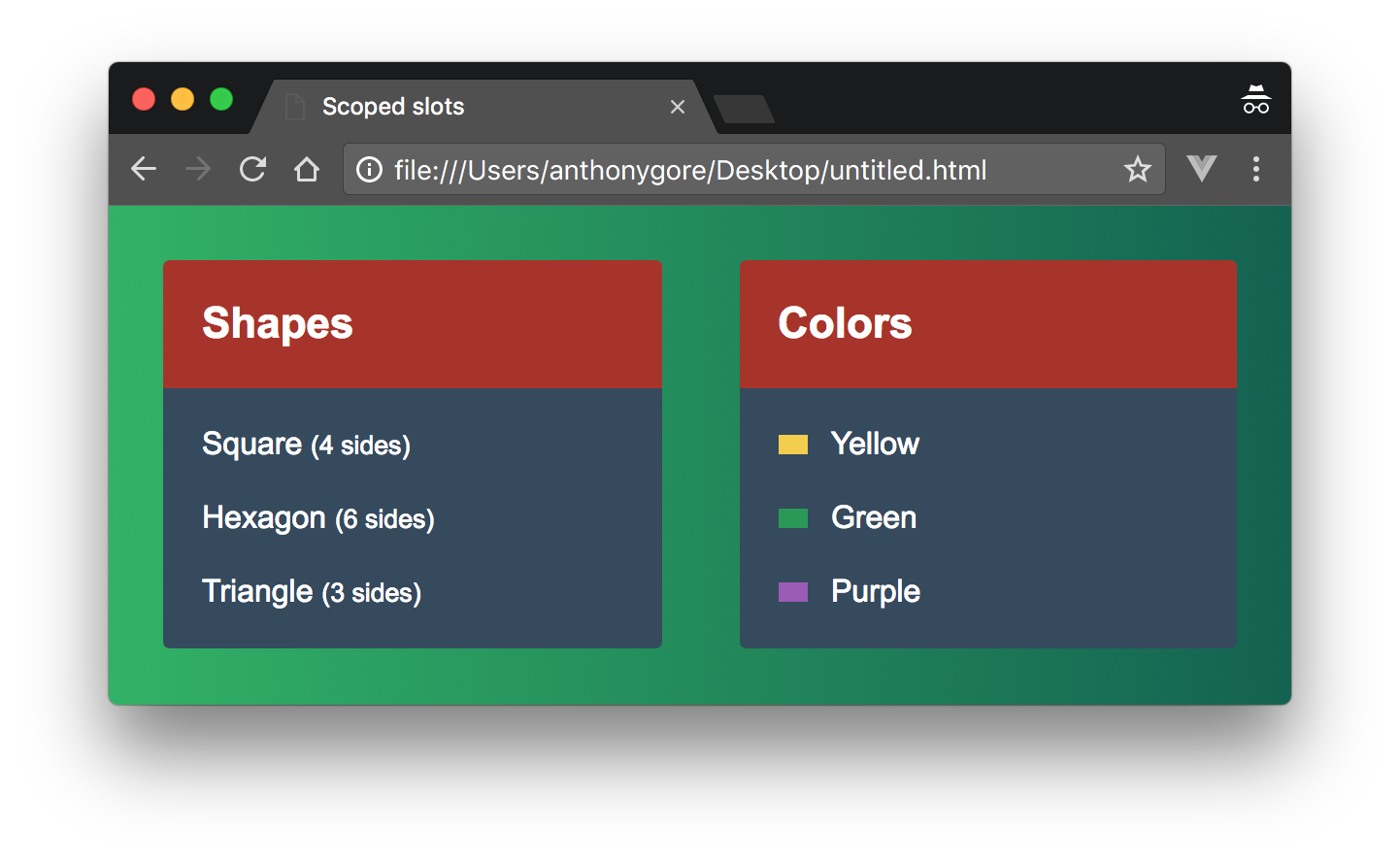
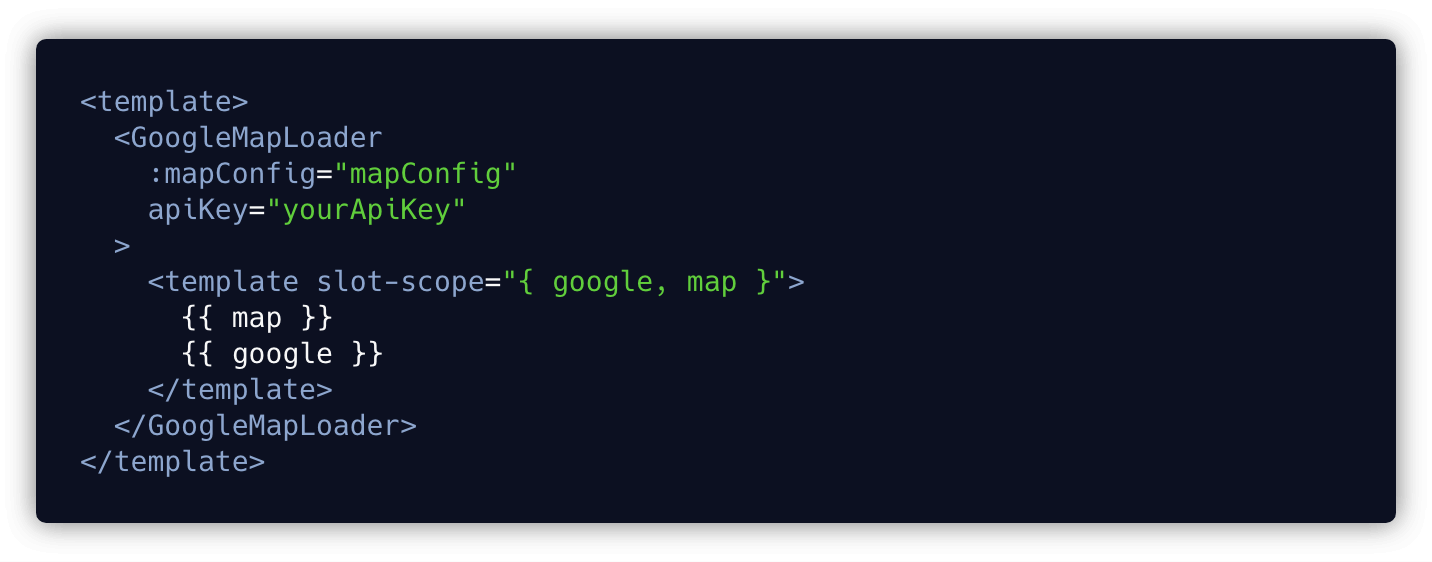
4. Scope slots
Sometimes we need to access the data inside the component when we call it and distribute content to its socket. The data in the component can be bound to the slot prop, and then the data on the slot prop can be accessed at the same time when the component is called.
Call the slot and use the value of the slot prop:
Multiple slot prop s can be set for slots:
Receive:
Slot prop can also be used for deconstruction:
Note:
If there are many slot props, it is recommended to integrate all data into one object and pass one slot prop.
Render function, JSX grammar and CreaeElement function


Render functions are the same as templates in creating html templates, but in some scenarios, the code implemented with templates is tedious and repetitive, so render functions can be used.
If render function is used in component rendering, then you can not use the < template > tag. Only < script > labels and < style > labels are required in component files.
Before we understand the render function, we need to define a concept of Vnode.
Vue Slot Props Method
1. Vnode (virtual node)
When using Vue to develop a project, the structure rendered on the browser is rendered on the browser by Vue through various conditions, loops, calculations and other operations of the underlying mechanism. We regard the final result rendered on the browser as a real DOM tree.
But Vue responds to data efficiently. Faced with such efficient data response, it is also necessary to update nodes in the page equally efficiently. However, the structure of DOM is very large and complex, and it is particularly difficult to complete all DOM updates.
For example, we render a merchandise management list. When a certain value of a commodity changes, the list rendering of the page also needs to be updated. If we want to use native JS to render, we may need to re-render the entire table, or a row. If you want to locate a cell accurately, the code is very demanding.
Fortunately, when using Vue, we don't need to update the DOM tree manually using JS. Vue provides a virtual DOM tree through which it can track how it wants to change the real DOM.
DOM nodes written in vue file and DOM in render function are virtual DOM. When browser renders, all virtual DOM will be calculated and rendered on browser finally.
When we create a virtual DOM, we include all the information of the virtual DOM, such as child elements, class names, styles, locations, and so on.
Vue instances provide render functions to render virtual DOM, and render function parameters (also a function) to create virtual DOM.
2. Example render function
The < Home > component can be called normally, and the < div > rendered by the render function is taken when it is called.
render function:
- The parameter is the ce function (which is written as createElement in many places).
- The return value is a VNode (node to be rendered).
3. Parameter of render function - createElement function
The parameter of render function is the createElement function, which creates VNode as the return value of render.
Vuetify Slot Props
The createElement function takes three parameters:
- Parametric 1:
String Object Function
An HTML tag name, component option object, or resolve has one of the async functions mentioned above. Required items. - Parametric 2:
Object
An object that contains all the relevant attributes of this tag (or template). Optional. - Parametric 3:
String Array
A child node or list created by createElement.
Following are detailed descriptions and examples of the second and third parameters of createElement:
4. JSX grammar
If the structure in a template is relatively simple, we can use the createElement function, but once the structure is slightly more complex, the code becomes particularly lengthy.
If you want to continue using render functions, you need to use JSX grammar. Because JSX grammar allows HTML structures to be written in JS code.

Vue Slot Props Example
JSX grammar may be more widely used in React.
Added by flyersun on Thu, 01 Aug 2019 08:48:09 +0300



